Abstract
Introduction:
Toxoplasmosis is a rare complication of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AlloHSCT) usually through reactivation in a previously seropositive recipient, and is associated with mortality as high as 60% (Paccoud et al. BMT 2020). Seroprevalence in the population varies ranging from 5% or lower in North America to over 50% in France. Risk factors for reactivation include immune suppression, seronegative donors, cord blood grafts, and lack of adequate antimicrobial prophylaxis (Robin et al. BBMT 2019). We sought to evaluate the outcomes of patients with toxoplasma reactivation after undergoing AlloHSCT in the modern era.
Methods:
This study was a retrospective single center analysis of all patients who underwent AlloHSCT between January 2012 and June 2021 at our center. Primary objectives were to assess the incidence of toxoplasma reactivation and the effects of reactivation on survival. Patients were identified in the department database and relevant demographic and clinical data were extracted. Results of toxoplasma testing [IgG serology and polymerase chain reaction (PCR)] were collected and verified by manual chart review. Patients with negative toxoplasma serology and/or missing serology or PCR data were excluded from analysis. Reactivation was defined as positive PCR in a seropositive patient. Toxoplasma reactivation associations were assessed by logistic regression models. Overall Survival (OS) was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and differences compared using the log-rank test. Cox proportional hazards models were used for survival associations. Cumulative incidence of non-relapse mortality (NRM) was determined using competing risks method. This study was approved by the institutional board review (IRB) committee at our center.
Results:
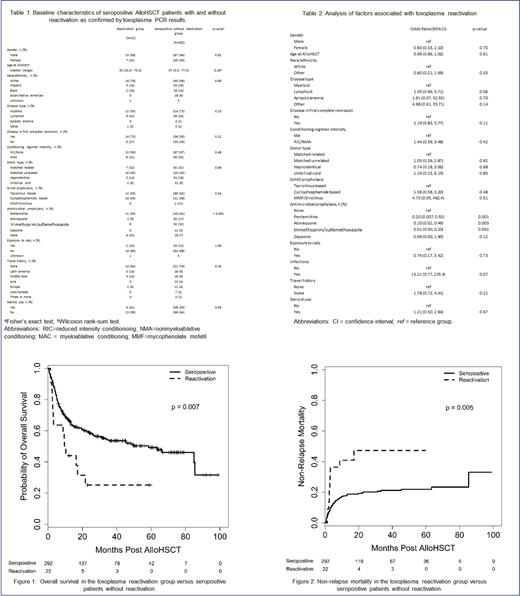
A total of 370 patients who received AlloHSCT and had a positive toxoplasma IgG were identified. Fifty-two patients had missing toxoplasma PCR and 4 did not meet eligibility criteria and were excluded. Twenty-two (7%) out of the remaining 314 seropositive patients experienced toxoplasma reactivation as confirmed by positive PCR. Median age in the reactivation group was 55 years, and patients were mostly white males with myeloid neoplasms who underwent AlloHSCT in first complete remission using nonmyeloablative conditioning and a matched unrelated donor (table 1). No significant differences in baseline characteristics were seen between the seropositive only and the reactivation groups, except for antimicrobial prophylaxis use (P <0.001). Fifty-nine percent of patients (13 out of 22) in the reactivation group were on toxoplasma prophylaxis compared to 93% (273 out of 292) in the seropositive patients without reactivation. Sixteen out of the 22 (73%) patients with reactivation developed clinical symptoms while 6 (27%) had asymptomatic reactivation. Antimicrobial prophylaxis only with either pentamidine, atovaquone, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole but not dapsone, was associated with lower risk of developing reactivation (table 2). With a median follow up of 15.4 months (0.3-98.9), the median OS was 9.6 months in patients with reactivation versus 58.5 months in seropositive patients without reactivation [HR, 2.06; (95% CI, 1.21 to 3.52); P=0.008] (figure 1). NRM was also higher in the reactivation group [HR, 2.61; (95% CI, 1.34 to 5.11); P=0.005] (figure 2). Specifically, day 100, 1-year and 2-year NRM were higher in the reactivation group versus (vs) seropositive patients (36% vs 10%, 41% vs 18%, and 47% vs 20% respectively). Toxoplasma reactivation was associated with worse OS and increased NRM in univariable analysis however this did not reach statistical significance in multivariable analysis.
Conclusion:
Toxoplasma reactivation in seropositive AlloSCT patients remains low at our center at around 7%. Toxoplasma reactivation is associated with worse outcomes after AlloHSCT and reactivation could be mitigated by improved compliance with antimicrobial prophylaxis.
Mehta: Kadmon: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; CSLBehring: Research Funding; Syndax: Research Funding. Shah: Amgen: Consultancy; Bluebird Bio: Research Funding; BMS/Celgene: Research Funding; CareDx: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Indapta Therapeutics: Consultancy; Janssen: Research Funding; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Kite: Consultancy; Nektar: Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Consultancy; Poseida: Research Funding; Precision Biosciences: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy; Sutro Biopharma: Research Funding; Teneobio: Research Funding. Hosing: Nkarta Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Rezvani: Pharmacyclics: Other: Educational grant, Research Funding; Affimed: Other: License agreement and research agreement; education grant, Patents & Royalties, Research Funding; Takeda: Other: License agreement and research agreement, Patents & Royalties; GSK: Other: Scientific Advisory Board ; Caribou: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; GemoAb: Other: Scientific Advisory Board ; AvengeBio: Other: Scientific Advisory Board ; Virogin: Other: Scientific Advisory Board ; Navan Technologies: Other: Scientific Advisory Board; Bayer: Other: Scientific Advisory Board . Qazilbash: Janssen: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Other: Advisory Board; Angiocrine: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Oncopeptides: Other: Advisory Board; Biolline: Research Funding; NexImmune: Research Funding. Popat: Bayer: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Shpall: Takeda: Patents & Royalties; Navan: Consultancy; Novartis: Honoraria; Magenta: Honoraria; Affimed: Patents & Royalties; Novartis: Consultancy; Magenta: Consultancy; Adaptimmune: Consultancy; Axio: Consultancy; Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria. Ahmed: Seagen: Research Funding; Xencor: Research Funding; Tessa Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal